- Microsoft SQL Server Express is a version of Microsoft's SQL Server relational database management system that is free to download, distribute and use. It comprises a database specifically targeted for embedded and smaller-scale applications.
- Get a free, entry-level SQL Server edition that’s ideal for deploying small databases in production environments with the Microsoft SQL Server 2017 Express edition.
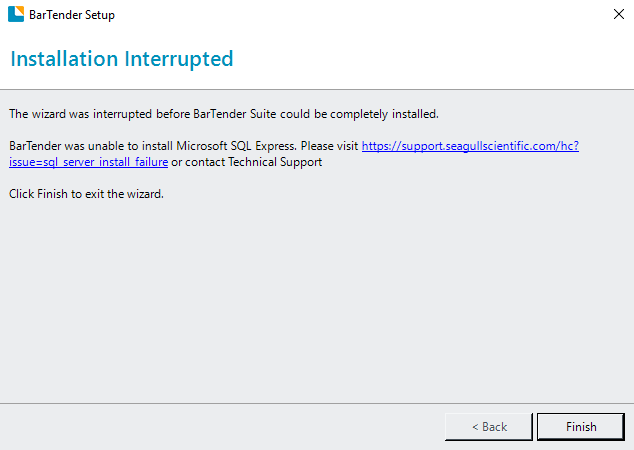
- I installed vs 2012 express. Now i want download sql server management studio 2012 express. But i have sql server 2012 express jun i need management studio 2012 express. The link that Sam Lester gave, goes to a webpage which says Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Express. This doesn't include the Managment Studio.
Download SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS); 4 minutes to read +22; In this article. APPLIES TO: SQL Server Azure SQL Database Azure SQL Data Warehouse Parallel Data Warehouse. SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is an integrated environment for managing any SQL infrastructure, from SQL Server to Azure SQL Database.
Microsoft SQL Server Express LocalDB is a feature of SQL Server Express targeted to developers. It is available on SQL Server Express with Advanced Services.
LocalDB installation copies a minimal set of files necessary to start the SQL Server Database Engine. Once LocalDB is installed, you can initiate a connection using a special connection string. When connecting, the necessary SQL Server infrastructure is automatically created and started, enabling the application to use the database without complex configuration tasks. Developer Tools can provide developers with a SQL Server Database Engine that lets them write and test Transact-SQL code without having to manage a full server instance of SQL Server.
Try it out!
- To download and install SQL Server Express LocalDB, go to SQL Server downloads. LocalDB is a feature you select during installation, and is available when you download the media. If you download the media, either choose Express Advanced or the LocalDB package. In the Visual Studio Installer, you can install SQL Server Express LocalDB as part of the .NET desktop development workload or as an individual component.
Tip
You can also install LocalDB as part of Visual Studio. During Visual Studio installation, select the .NET desktop development workload, which includes SQL Server Express LocalDB.
- Have an Azure account? Get started and spin up a virtual machine with SQL Server 2016 (13.x) already installed.
Install LocalDB

Install LocalDB through the installation wizard or by using the SqlLocalDB.msi program. LocalDB is an option when installing SQL Server 2016 Express.
Select LocalDB on the Feature Selection/Shared Features page during installation. There can be only one installation of the LocalDB binary files for each major SQL Server Database Engine version. Multiple Database Engine processes can be started and will all use the same binaries. An instance of the SQL Server Database Engine started as the LocalDB has the same limitations as SQL Server Express.
An instance of SQL Server Express LocalDB is managed by using the SqlLocalDB.exe utility. SQL Server Express LocalDB should be used in place of the SQL Server Express user instance feature, which was deprecated.
Description
The LocalDB setup program uses the SqlLocalDB.msi program to install the necessary files on the computer. Once installed, LocalDB is an instance of SQL Server Express that can create and open SQL Server databases. The system database files for the database are stored in the local AppData path, which is normally hidden. For example, C:Users<user>AppDataLocalMicrosoftMicrosoft SQL Server Local DBInstancesLocalDBApp1. User database files are stored where the user designates, typically somewhere in the C:Users<user>Documents folder.
For more information about including LocalDB in an application, see Visual Studio Local Data Overview, Create a database and add tables in Visual Studio.
For more information about the LocalDB API, see SQL Server Express LocalDB Reference.
The SqlLocalDb utility can create new instances of LocalDB, start and stop an instance of LocalDB, and includes options to help you manage LocalDB.For more information about the SqlLocalDb utility, see SqlLocalDB Utility.
The instance collation for LocalDB is set to SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS and cannot be changed. Database-level, column-level, and expression-level collations are supported normally. Contained databases follow the metadata and tempdb collations rules defined by Contained Database Collations.
Restrictions
LocalDB cannot be a merge replication subscriber.
LocalDB does not support FILESTREAM.
LocalDB only allows local queues for Service Broker.
An instance of LocalDB owned by the built-in accounts such as
NT AUTHORITYSYSTEMcan have manageability issues due to windows file system redirection. Instead use a normal windows account as the owner.
Automatic and named instances
LocalDB supports two kinds of instances: Automatic instances and named instances.
Automatic instances of LocalDB are public. They are created and managed automatically for the user and can be used by any application. One automatic instance of LocalDB exists for every version of LocalDB installed on the user's computer. Automatic instances of LocalDB provide seamless instance management. There is no need to create the instance; it just works. This feature allows for easy application installation and migration to a different computer. If the target machine has the specified version of LocalDB installed, the automatic instance of LocalDB for that version is available on the target machine as well. Automatic instances of LocalDB have a special pattern for the instance name that belongs to a reserved namespace. Automatic instances prevents name conflicts with named instances of LocalDB. The name for the automatic instance is MSSQLLocalDB.
Named instances of LocalDB are private. They are owned by a single application that is responsible for creating and managing the instance. Named instances provide isolation from other instances and can improve performance by reducing resource contention with other database users. Named instances must be created explicitly by the user through the LocalDB management API or implicitly via the app.config file for a managed application (although managed application may also use the API, if desired). Each named instance of LocalDB has an associated LocalDB version that points to the respective set of LocalDB binaries. The instance name of a LocalDB is sysname data type and can have up to 128 characters. (This differs from regular named instances of SQL Server, which limits names to regular NetBIOS names of 16 ASCII chars.) The name of an instance of LocalDB can contain any Unicode characters that are legal within a filename.A named instance that uses an automatic instance name becomes an automatic instance.
Different users of a computer can have instances with the same name. Each instance is a different processes running as a different user.
Shared instances of LocalDB
To support scenarios where multiple users of the computer need to connect to a single instance of LocalDB, LocalDB supports instance sharing. An instance owner can choose to allow the other users on the computer to connect the instance. Both automatic and named instances of LocalDB can be shared. To share an instance of LocalDB, a user selects a shared name (alias) for it. Because the shared name is visible to all users of the computer, this shared name must be unique on the computer. The shared name for an instance of LocalDB has the same format as the named instance of LocalDB.
Only an administrator on the computer can create a shared instance of LocalDB. A shared instance of LocalDB can be unshared by an administrator or by the owner of the shared instance of LocalDB. To share and unshared an instance of LocalDB, use the LocalDBShareInstance and LocalDBUnShareInstance methods of the LocalDB API, or the share and unshared options of the SqlLocalDb utility.
Start LocalDB and connect to LocalDB
Connect to the automatic instance
The easiest way to use LocalDB is to connect to the automatic instance owned by the current user by using the connection string Server=(localdb)MSSQLLocalDB;Integrated Security=true. To connect to a specific database by using the file name, connect using a connection string similar to Server=(LocalDB)MSSQLLocalDB; Integrated Security=true ;AttachDbFileName=D:DataMyDB1.mdf.
Note
The first time a user on a computer tries to connect to LocalDB, the automatic instance must be both created and started. The extra time for the instance to be created can cause the connection attempt to fail with a timeout message. When this happens, wait a few seconds to let the creation process complete, and then connect again.
Create and connect to a named instance
In addition to the automatic instance, LocalDB also supports named instances. Use the SqlLocalDB.exe program to create, start, and stop a named instance of LocalDB. For more information about SqlLocalDB.exe, see SqlLocalDB Utility.
The last line above, returns information similar to the following.
| Name | LocalDBApp1 |
| Version | <Current Version> |
| Shared name | ' |
| Owner | '<Your Windows User>' |
| Auto create | No |
| State | running |
| Last start time | <Date and Time> |
| Instance pipe name | np:.pipeLOCALDB#F365A78Etsqlquery |
Microsoft Sql Server Express 2012 64 Bit
Note
If your application uses a version of .NET before 4.0.2 you must connect directly to the named pipe of the LocalDB. The Instance pipe name value is the named pipe that the instance of LocalDB is listening on. The portion of the Instance pipe name after LOCALDB# will change each time the instance of LocalDB is started. To connect to the instance of LocalDB by using SQL Server Management Studio, type the instance pipe name in the Server name box of the Connect to Database Engine dialog box. From your custom program you can establish connection to the instance of LocalDB using a connection string similar to SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(@'Server=np:.pipeLOCALDB#F365A78Etsqlquery');
Connect to a shared instance of LocalDB
To connect to a shared instance of LocalDB add . (backslash + dot + backslash) to the connection string to reference the namespace reserved for shared instances. For example, to connect to a shared instance of LocalDB named AppData use a connection string such as (localdb).AppData as part of the connection string. A user connecting to a shared instance of LocalDB that they do not own must have a Windows Authentication or SQL Server Authentication login.
Troubleshooting
For information about troubleshooting LocalDB, see Troubleshooting SQL Server 2012 Express LocalDB.
Permissions
An instance of SQL Server 2016 ExpressLocalDB is an instance created by a user for their use. Any user on the computer can create a database using an instance of LocalDB, store files under their user profile, and run the process under their credentials. By default, access to the instance of LocalDB is limited to its owner. The data contained in the LocalDB is protected by file system access to the database files. If user database files are stored in a shared location, the database can be opened by anyone with file system access to that location by using an instance of LocalDB that they own. If the database files are in a protected location, such as the users data folder, only that user, and any administrators with access to that folder, can open the database. The LocalDB files can only be opened by one instance of LocalDB at a time.
Note
LocalDB always runs under the users security context; that is, LocalDB never runs with credentials from the local Administrator's group. This means that all database files used by a LocalDB instance must be accessible using the owning user's Windows account, without considering membership in the local Administrators group.
See Also
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Stable release | SQL Server 2017 Express / November 6, 2017; 22 months ago |
| Written in | C, C++ |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows, Linux |
| Platform | IA-32 or IA-64 > 512 MB RAM .NET Framework 4.0[1] |
| Available in | English, Chinese, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese (Brazil), Russian, Spanish |
| Type | Relational database management system |
| License | Proprietary software[2] |
| Website | www.microsoft.com |
Microsoft Sql Server Express 2012 Sp2
Microsoft SQL Server Express is a version of Microsoft's SQL Serverrelational database management system that is free to download, distribute and use. It comprises a database specifically targeted for embedded and smaller-scale applications. The product traces its roots to the Microsoft Database Engine (MSDE) product, which was shipped with SQL Server 2000. The 'Express' branding has been used since the release of SQL Server 2005.
Capabilities[edit]
SQL Server Express provides many of the features of the paid, full versions of Microsoft SQL Server database management system.[3] However it has technical restrictions that make it unsuitable for some large-scale deployments. Differences in the Express product include:
- Maximum database size of 10 GB per database in SQL Server 2016, SQL Server 2014, SQL Server 2012, and 2008 R2 Express[4] (4 GB for SQL Server 2008 Express and earlier; compared to 2 GB in the former MSDE). The limit applies per database (log files excluded); but in some scenarios users can access more data through the use of multiple interconnected databases.
- No SQL Server Agent service[5][6]
- Artificial hardware usage limits:
- Single physical CPU, but multiple cores allowable[7]
- 1 GB of RAM (runs on a system with higher RAM amount, but uses only at most 1 GB per instance of SQL Server Database Engine. 'Recommended: Express Editions: 1 GB All other editions: At least 4 GB and should be increased as database size increases to ensure optimal performance.'[8]).[9] Express with Advanced Services has a limit of 4 GB per instance of Reporting Services (not available on other Express variants). Analysis Services is not available for any Express variant.
Unlike the predecessor product, MSDE, the Express product does not include a concurrent workload-governor to 'limit performance if the database engine receives more work than is typical of a small number of users.'[10]
SQL Server Express includes several GUI tools for database management. These include:
- SQL Server Management Studio - since 2012 SP1;[11] before that, only a stripped-down version called SQL Server Management Studio Express is provided
- SQL Server Configuration Manager
- SQL Server Surface Area Configuration tool
- SQL Server Business Intelligence Development Studio
The predecessor product MSDE generally lacked basic GUI management tools,[12]
Features available in SQL Server 'Standard' and better editions but absent from SQL Server Express include:
Variants[edit]
Microsoft makes SQL Server Express available as:
- An integrated edition with management tools
- Core database-engine only
- A SQL Server Express with Advanced Services edition (first introduced relatively late in Q2 2006 compared to the original release) with a reduced-functionality version of SQL Server Reporting Services and with full-text search capabilities
In the Free 2005 Express version, for example, a standard approach to installation options was provided, as follows.Generally, the SQL 2005 Express installers are packaged with the following consistent naming convention:
- SQLEXPR.EXE
- Has installers for BOTH 32-bit and 64-bit processors, but is a basic install
- SQLEXPR32.EXE
- Has ONLY the installer for 32-bit processors (still the basic install)
- SQLEXPRWT.EXE
- Has installers for BOTH 32-bit and 64-bit processors and SQL Server Management Studio Express (SSMSE) (2008 R2)
- SQLEXPR_ADV.EXE
- Has the basics and SQL Server Management Studio Express (SSMSE) + Reporting and Full Text Queries
- SQLEXPR_TOOLKIT.EXE
- Has the basics and SSMSE and Business Intelligence Development Studio (BIDS)
These optional variants have gone through several service packs (SP), and each SP installer can be used without using the older ones first:
- Originals of the above files all carry the version number 9.0.1399.6
- Service Pack 2 (SP2) versions all carry the version number 9.0.3042
- Service Pack 3 (SP3) versions all carry the version number 9.00.4035
- Service Pack 4 (SP4) versions all carry the version number 9.00.5000
Version history[edit]
| Version | Release date | Mainstream Support End Date | Extended Support End Date | Supported Operating Systems |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Server 2005 Express Edition | 2005-11-07[13] | 2011-04-12[14] | 2016-04-12[14] | Windows 2000 Service Pack 4, Windows XP Service Pack 2, Windows Server 2003 Service Pack, Windows 7 Service Pack 1 (only SQL Server 2005 Express Edition SP4)[15] |
| SQL Server 2008 Express | 2009-02-08[16] | 2014-07-08[17] | 2019-07-09[17] | Windows XP Service Pack 2, Windows XP Service Pack 3, Windows Vista, Windows Vista Service Pack 1, Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2, Windows Server 2008[18] |
| SQL Server 2008 R2 Express | 2010-04-16[19] | 2014-07-08[20] | 2019-07-09[20] | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2[21] |
| SQL Server 2012 Express | 2012-05-14[22] | 2017-07-11[23] | 2022-07-12[23] | Windows Vista Service Pack 2, Windows 7, Windows 7 Service Pack 1, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008,[24] Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2[25] |
| SQL Server 2014 Express | 2014-04-01[26] | 2019-07-09[27] | 2024-07-09[27] | Windows 7 Service Pack 1, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server 2008 SP2,[28] Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2[29] |
| SQL Server 2016 Express | 2016-06-01[30] | 2021-07-13[31] | 2026-07-14[31] | Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 |
| SQL Server 2017 Express | 2017-09-29[32] | 2022-10-11[33] | 2027-10-12[33] | Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016*, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3 or 7.4, SUSE Enterprise Linux Server v12 SP2, Ubuntu 16.04LTS, Docker Engine 1.8+ (on Windows, Mac, or Linux) |
- Does not include Windows Server 2016 'Essentials' Edition
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^'Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing SQL Server 2014 - SQL Server | Microsoft Docs'. Msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2019-04-03.
- ^'About the SQL Server License Terms - SQL Server | Microsoft Docs'. Msdn.microsoft.com. 2017-05-24. Retrieved 2019-04-03.
- ^Disable SQL Server VSS Writer service.
- ^'Features Supported by the Editions of SQL Server 2008 R2'. Retrieved 2010-06-22.
- ^'Compare Edition Features'.
- ^'SQL Server Express with Advanced Services Features'. Microsoft. Retrieved 28 March 2012.
- ^'How SQL Server 2005 Express Edition determines the CPU count and uses the CPUs during processing'. MSDN. November 2008. Retrieved 2008-11-25.
- ^'Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing SQL Server 2014 - SQL Server | Microsoft Docs'. Msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2019-04-03.
- ^'Editions and supported features of SQL Server 2016 - SQL Server | Microsoft Docs'. Msdn.microsoft.com. 2017-05-24. Retrieved 2019-04-03.
- ^'The SQL Server 2000 Workload Governor'. MSDN. January 2004. Retrieved 2007-01-15.
- ^'Download Microsoft® SQL Server® 2012 Service Pack 1 (SP1) Express from Official Microsoft Download Center'. Microsoft.com. 2012-11-09. Retrieved 2019-04-03.
- ^'How do I Manage SQL Server'. Archived from the original on 2010-07-24.
- ^'Download Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express Edition from Official Microsoft Download Center'. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ^ ab'Microsoft Support Lifecycle (SQL Server 2005)'. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ^'Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express Edition'. Microsoft Download Center. Retrieved 2017-04-07.
- ^'Download Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Express from Official Microsoft Download Center'. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ^ ab'Microsoft Support Lifecycle (SQL Server 2008)'. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ^'Download Microsoft® SQL Server® 2008 Express from Official Microsoft Download Center'. Microsoft.com. 2009-02-08. Retrieved 2019-04-03.
- ^'Download Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 - Express from Official Microsoft Download Center'. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ^ ab'Microsoft Support Lifecycle (SQL Server 2008 R2)'. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ^'Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing SQL Server 2008 R2'. msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2017-10-16.
- ^'Download Microsoft® SQL Server® 2012 Express from Official Microsoft Download Center'. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ^ ab'Microsoft Support Lifecycle (SQL Server 2012)'. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ^'Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing SQL Server 2012'. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- ^'Microsoft® SQL Server® 2012 SP2 Express'. Microsoft Download Center. Retrieved 2017-04-07.
- ^'Download Microsoft SQL Server 2014 Express'. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ ab'Microsoft Support Lifecycle (SQL Server 2014)'. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^'Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing SQL Server 2014'. Retrieved 30 June 2017.
- ^'Microsoft® SQL Server® 2014 Express'. Microsoft Download Center. Retrieved 2017-04-08.
- ^'Download Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Express'.
- ^ ab'Microsoft Support Lifecycle (SQL Server 2016)'.
- ^'Download Microsoft SQL Server 2017 Express'.
- ^ ab'Microsoft Support Lifecycle (SQL Server 2017)'.